Note that the value of investment assets at the end of 5th year (i.e. $50m) is the sum of scrap value ($10 m) and working capital ($40 m). GoCardless helps you automate payment collection, cutting down on the amount of admin your team needs to deal with when chasing invoices. Calculating ARR revenue is a good idea if you’re considering whether to invest in an expensive piece of machinery or equipment, or whether a new project will pay off in the long run. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
Accounting Rate of Return
It’s simpler than you might imagine, and it can offer powerful insights into your business. As the ARR exceeds the target return on investment, the project should be accepted. Remember that you may need to change these details depending on the specifics of your project. Overall, however, this is a simple and efficient method for anyone who wants to learn how to calculate Accounting Rate of Return in Excel.
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) Formula
It encompasses all types of recurring revenue, such as subscriptions, membership fees, and license fees, offering a more precise view of your company’s long-term growth potential. However, the formula doesn’t take the cash flow of a project or investment into account. It should therefore always be used alongside other metrics to get a more rounded and accurate picture. ARR takes into account any potential yearly costs for the project, including depreciation. Depreciation is a practical accounting practice that allows the cost of a fixed asset to be dispersed or expensed. This enables the business to make money off the asset right away, even in the asset’s first year of operation.
ARR vs. MRR: What is the Difference?
The operating expenses of the equipment other than depreciation would be $3,000 per year. The new machine would increase annual revenue by $150,000 and annual operating expenses by $60,000. The estimated useful life of the machine is 12 years with zero salvage value. The denominator in the formula is the amount of investment initially required to purchase the asset. If an old asset is replaced with a new one, the amount of initial investment would be reduced by any proceeds realized from the sale of old equipment. ARR illustrates the impact of a proposed investment on the accounting profitability which is the primary means through which stakeholders assess the performance of an enterprise.
Common Mistakes in ARR Calculation
It offers a solid way of measuring financial performance for different projects and investments. Like any other financial indicator, ARR has its advantages and disadvantages. Evaluating the pros and cons of ARR enables stakeholders to arrive at informed decisions about its acceptability in some investment circumstances and adjust their approach to analysis accordingly. It’s important to understand these differences for the value one is able to leverage out of ARR into financial analysis and decision-making. Here we are not given annual revenue directly either directly yearly expenses and hence we shall calculate them per the below table. In order to properly calculate the metric, one-time fees such as set-up fees, professional service (or consulting) fees, and installation costs must be excluded, since they are one-time/non-recurring.
The Accounting Rate of Return is the overall return on investment for an asset over a certain time period. We are given annual revenue, which is $900,000, but we need to work out yearly expenses. In both months, the churn rate and expansion ARR will be estimated as 6% and 2% respectively. The ARR multiple is a method to quantify the implied valuation of a SaaS company into a valuation multiple, facilitating comparisons to peer companies and the industry benchmark.

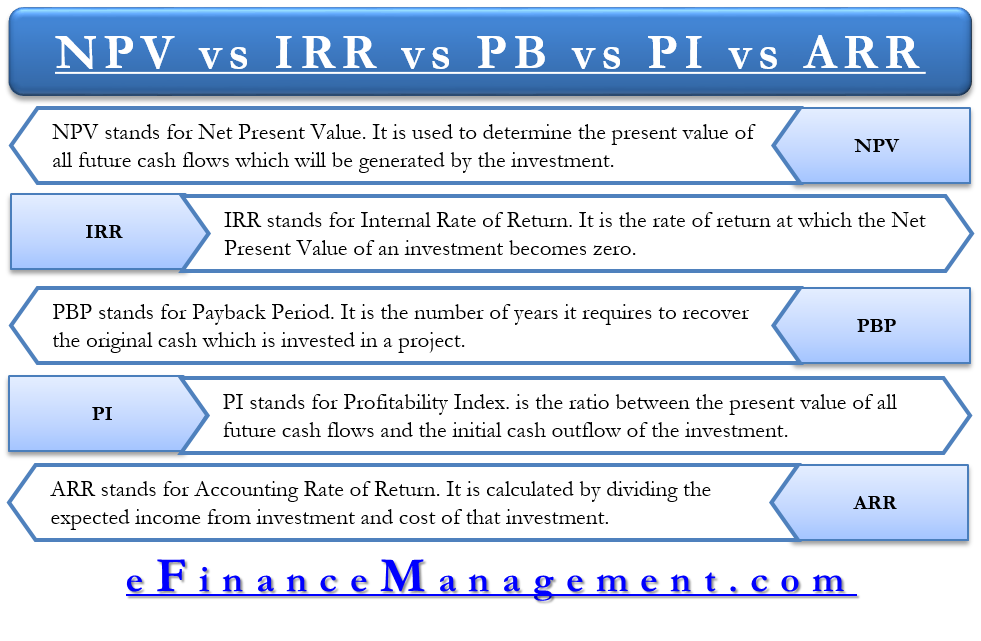
The ARR is the annual percentage return from an investment based on its initial outlay. The required rate of return (RRR), or the hurdle rate, is the minimum return an investor would accept for an investment or project that compensates them for a given level of risk. It is calculated using the dividend discount model, which accounts for stock price changes, or the capital asset pricing model, which compares returns to the market. The accounting rate of return is a capital budgeting metric to calculate an investment’s profitability. Businesses use ARR to compare multiple projects to determine each endeavor’s expected rate of return or to help decide on an investment or an acquisition. If you have already studied other capital budgeting methods (net present value method, internal rate of return method and payback method), you may have noticed that all these methods focus on cash flows.
- Therefore, the implied ARR multiple at which Hebbia raised its Series B funding comes out to approximately 54x, reflecting the market size and revenue opportunity of the one of the top Gen AI startups at present.
- To figure out the Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) for your SaaS business, you must first understand what recurring revenue is.
- Very often, ARR is preferred because of its ease of computation and straightforward interpretation, making it a very useful tool for business owners, key stakeholders, finance teams and investors.
- It’s simpler than you might imagine, and it can offer powerful insights into your business.
- In this guide, we’ll cover how to calculate ARR as well as what to do with this information.
Recurring revenue, a crucial part of this calculation, consists of income from customer subscriptions, upgrades, and other similar ongoing sources. However, one-time payments do not count as recurring revenue because they do not guarantee repetition. An ARR of 10% for example means that the investment would generate an average of 10% annual accounting profit over the investment period based on the average investment.
Here, the average annual profit stands at $70,000, and the initial investment is $250,000. This suggests the business can expect a 28% return on its investment annually. The key distinction between Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) and Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) lies in their frequency of revenue measurement.
Further management uses a guideline such as if the accounting rate of return is more significant than their required quality, then the project might be accepted else not. Conceptually, the ARR metric can be thought of as the annualized MRR of subscription-based businesses. Since ARR represents the revenue expected to repeat into the future, the metric is most useful for tracking trends and predicting growth, as well as for identifying the strengths (or weaknesses) of the company. ARR stands for “Annual Recurring Revenue” and represents a company’s subscription-based revenue expressed on an annualized basis. Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) estimates the predictable revenue generated per year by a SaaS company from customers on either a subscription plan or a multi-year contract. To predict Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) growth, start by reviewing the previous year’s performance, particularly the ARR.
Such inconsistent practices can cause discrepancies in ARR calculations, leading to confusion and misinterpretation of your startup’s financial and operational performance. Let’s discuss churn – the situation where customers terminate their subscriptions. doc chapter 5 activity The revenue lost from these cancellations should be deducted from your total annual subscription revenue to calculate ARR. Moreover, you should also consider any downgrades where customers choose a less expensive subscription plan.