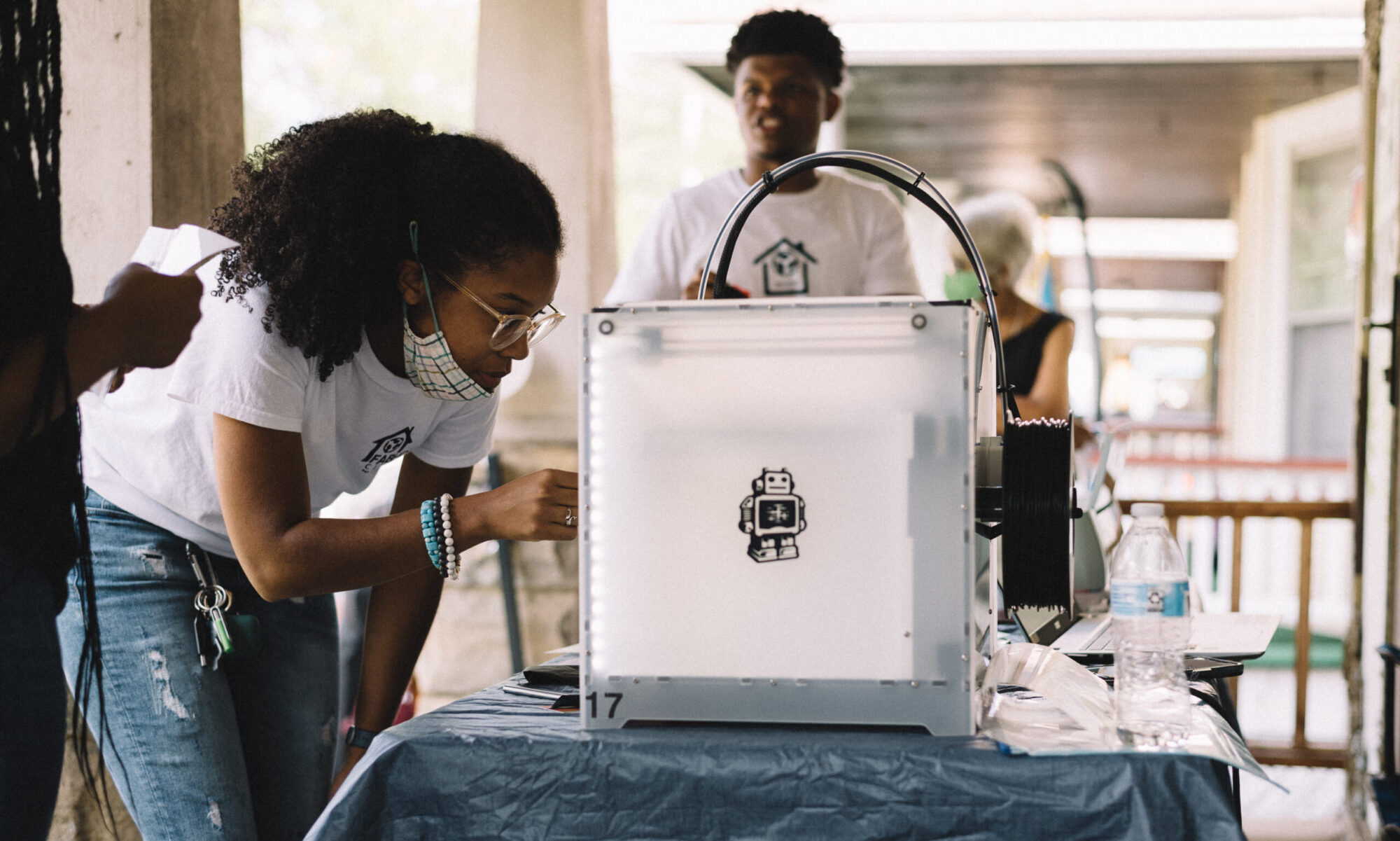
Many options chains such as those at the best brokers for options trading provide the implied volatility for each contract. From the example above, if the volatility in WBA is 23.6%, we look back over the past 30 days and observe that the historical volatility is calculated to be 23.5%, which is a moderate level of volatility. If a trader compares this to the current implied volatility, the trader should become aware that there may or may not be an event that could affect the stock’s price. When traders buy or sell options, they’re not just gaining exposure to the direction of the stock price, but also on how much the price might fluctuate (in either direction) before the option expires.
Is high IV good or bad?
While this makes the formula quite valuable to traders, it does require complex mathematics. Fortunately, traders and investors who use it do not need to do these calculations. Finally, implied volatility is often used as a heuristic gauge of market sentiment–particularly fear and uncertainty. When markets are calm and traders are complacent, implied volatility tends to be low. But when there’s a lot of uncertainty or concern about potential risks, implied volatility can spike higher.
For example, when IV is significantly above its average, it might be a good time to consider selling options to collect premium before the market calms down. During market drops, the VIX rises as more traders demand options on the S&P 500 because they expect equally violent snapbacks. When uncertainty is high, such as before earnings or major announcements, IV increases, and options become more expensive. Higher IV means wider expected ranges from the stock price, which means delta values are spread out much more than in a low IV environment.
Now, you could how to invest after you retire find contracts with lower premiums – but these typically have a lower likelihood of ending up in the money. But beyond your specific options trading strategy, it’s important to note that there is a direct correlation between IV and profitability. Understanding implied volatility is important for options traders for several reasons. If you’re searching for implied volatility options meaning, you’ve come to the right place.
It can’t what a stockbroker does and how to become one be emphasized enough, however, that implied volatility is what the marketplace expects the stock to do in theory. And as you probably know, the real world doesn’t always operate in accordance with the theoretical world. Some traders can trade both very well, but I think most traders find one side of the market easier to manage, based on their risk tolerance and personality. This type of situation impacts long and short Vega traders very differently. As you can see in the graph below, volatility tends to gradually drift sideways / lower, and then shoot up over a short period of time. With that said, let’s look at the portfolio again, but this time, instead of the short strangle on NFLX, the trader is using a calendar spread.
What Is Implied Volatility In Options? How To Calculate It Here
With stocks, you can make money if the stock moves up or down; but options provide such amazing flexibility, you can profit in a multitude of different environments. Spread bets and CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 69% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading spread bets and CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how spread bets and CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Brokers to Consider for Using Implied Volatility in Options Trading Strategies
This overestimation of future volatility can create opportunities for options sellers, as the fear of uncertainty often leads to inflated options prices. The first IV represents the market’s expectations for future price movement. It doesn’t tell you which direction an asset will move but how much movement traders expect.
VIX traded steadily between 16 and 22 for the period shown, other than the brief spike up to 30 after the earthquake. Take a look at the chart below and notice what happened to What happens when a stock splits volatility over that period. That might be above your risk tolerance, so you could look at swapping out one of the strategies.
- That’s why spikes in the VIX don’t last very long, and IV returns to normal after a company releases earnings.
- Implied volatility (IV) is the level of volatility of the underlying implied by the current option price.
- That’s the fascinating part about implied volatility and how it can be used by a trader to understand expected moves in the market.
- However, implied volatility is not solely determined by historical volatility.
Implied volatility is important because it can impact the price of options and other derivatives. Implied volatility is a measure of the market’s expectation for the future volatility of a financial instrument, such as a stock or option. Long Vega trades have a tendency to decay over time as volatility drifts sideways, so there is a cost of carry while these traders wait around for a market shock. Such things as a bad economic report, like GDP coming in well below expected, or a currency crisis, can result in a short, sharp spike in volatility, as traders panic and begin to close out positions. The trader thinks he is diversified, because he is trading 4 different stocks and 4 different strategies. It’s all well and good estimating a stock’s range over 12 months, but not many people trade 12-month options.
Implied volatility is the level of volatility of the underlying asset implied by the current option price. The premier site for active option and equity traders, providing the fastest, most thorough, and accurate options analytics in the industry. OptionsHawk is the first, and best, site to provide real-time analysis of Institutional and Unusual options trades. Some traders mistakenly believe that volatility is based on a directional trend in the stock price.